Protocol
What is Protocol?Protocol is the set of rules used in digital communication to ensure the systematic and safe transfer of data over the network. Everything you send or receive on the internet is work according to the protocols. All these protocols are exist in the seven layers of the OSI model.
What is Topology?
Methods are used to inter-connect two or more devices is called Topology.
Example:- we are using wires to connect the devices and how much wires it took and which pattern we used to connect to each other is called topology.
Types of Topology:-
1. Bus Topology
This is the diagram of the Bus Topology. As you can see it has two Terminator or we call it as two ends. In this topology what happens, if we are sending the data to the Device-3 on that time all other connections will be get inactive automatically and data directly will enter to the Device-3.
(Or)
If we are sending the data to the Device-7 on that time all other connections will be get inactive automatically and data directly will enter to the Device-7.
2. Ring Topology
This is the diagram of the Ring Topology. This topology will work in a circle form as it diagram. In this topology the data will transfer and collected by the clock wise. Like if Device-1 wants to send data to the Device-5 then Device-1 will transfer the data to Device-2, then Device-2 will send to Device-3, then Device-3 will send to Device-4, and then Device-4 will send to the Device-5 finally.
If you Device-5 wants to send some data to Device-1 then Device-5 will transfer the data to Device-6, then Device-6 will send to Device-7, then Device 7 will send to Device-8, and then finally Device-1 will get the data.
It works only in clock wise.
It never works in anti-clock wise.
3. Star Topology
4. Mess Topology
5. Tree Topology or Hybrid Topology
What is OSI Reference model?
Full form of OSI model is Open System Inter-connection model (or) Open System Inter-Change model. Prepared by International Standard Organization (ISO). There are seven layers in OSI model, there are:-
1. Application Layer:- This will directly interact with user and this is the only layer which can interact with the user. This is also called as Desktop Layer. This will provide E-mail Services, File Transfer Services, Directory Services, Network Management Services, Websites, Games etc... user will give command tho this application layer and then application layer will give to presentation layer and presentation layer will give to session layer and it goes on to the seven layer of OSi Reference Model, all seven layer will work together by distributing the services and get results to the user which he needs.
✱ Conjunction Control or Flow Control
It will control the speed of the sending and receiving of data and also measures the time of transmission of data.. Because in some cases receiver has less speed of data transmission and sender has more speed of data transmission, in that case receiver can't bear it and data will be corrupted. So, on this case Flow Control will control the data transmission at the same speed to the both side.
There are two types of internet protocols
1. IPv4
✱ This is 32bit.
✱ This will only connect 4,294,967,295 Devices which is (2^32)
✱ This is consist of four numbers represented by dots
✱ Each number can range from 0 to 255 in decimal numbers, Also it is converted to binary code internally to make computer understandable.
✱ Each number is represented by group of eight binary digits
✱ Total IPv4 is represented by 32 ones and zero's
2. IPv6
✱ This is128 bit.
✱ This can connect 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 which is (2^128)
✱ Total IPv6 is represented by 128 ones and zero's
✱ This is human friendly
Classification of IP Address?
1. Dynamic IP Address:- This type of IP Address is not permanent it will always get change automatically when we disconnect and connect it again. It has very strong security.
2. Static IP Address:- This type of IP Address is permanent i will never change. It has less security.
(Or)
If we are sending the data to the Device-7 on that time all other connections will be get inactive automatically and data directly will enter to the Device-7.
2. Ring Topology
If you Device-5 wants to send some data to Device-1 then Device-5 will transfer the data to Device-6, then Device-6 will send to Device-7, then Device 7 will send to Device-8, and then finally Device-1 will get the data.
It works only in clock wise.
It never works in anti-clock wise.
3. Star Topology
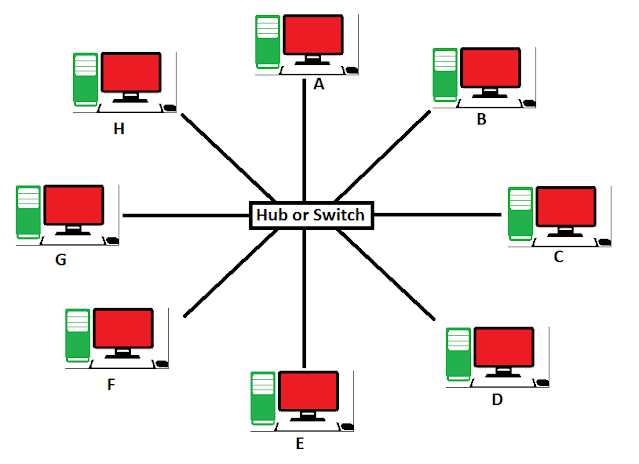
This is the diagram of the Star Topology. In this topology HUB will controls all the work stations. In this topology if any device wants to transfer the data to any other device, then it should first transfer to the HUB with the delivery location,then HUB will verify and then it will transfer the data to that device location. Like, if Device-C wants to transfer the data to the Device-H, then the Device-C has to transfer the data to the HUB first, and then HUB will transfer the data to the Device-H.
This is the diagram of the Mess Topology. In this topology every device was connected to the each other. So, any device can send the data to the any device directly.
5. Tree Topology or Hybrid Topology
This is the diagram of the Tree Topology or Hybrid Topology. When the two or more topology's are in one topology then it's called Tree Topology or Hybrid Topology. In this topology again HUB will controls all the devices, HUB is the head of these all devices.
In this topology if Device-B wants to send the data to the Device-8, the Device-B will send the data to the HUB with the delivery address, then HUB will verify and again send it to the Device-E and then finally Device-E will send the data to the Device-8.
In this topology if Device-B wants to send the data to the Device-8, the Device-B will send the data to the HUB with the delivery address, then HUB will verify and again send it to the Device-E and then finally Device-E will send the data to the Device-8.
What is OSI Reference model?
Full form of OSI model is Open System Inter-connection model (or) Open System Inter-Change model. Prepared by International Standard Organization (ISO). There are seven layers in OSI model, there are:-
1. Application Layer:- This will directly interact with user and this is the only layer which can interact with the user. This is also called as Desktop Layer. This will provide E-mail Services, File Transfer Services, Directory Services, Network Management Services, Websites, Games etc... user will give command tho this application layer and then application layer will give to presentation layer and presentation layer will give to session layer and it goes on to the seven layer of OSi Reference Model, all seven layer will work together by distributing the services and get results to the user which he needs.
2. Presentation Layer
✱ Translation:- This will translate the data to the opposite side.
Example:- two computers are there A & B, now Computer-A can only understand ASCII language and it will also transmit the data in ASCII language only and Computer-B can only understand EBCDIC language and it will also transmit the data in EBCDIC language only obviously, then translation will translate ASCII to EBCDIC, EBCDIC to ASCII.
ASCII:- Amecian Standard Code for Information Interchange
EBCDIC:- Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
✱ Encryption & Decryption:- This is a type of END to END Encryption, Here what will happen when we are sending any data like am sending "hello" to my friend, then while transferring this data hello to my friend the hacker can read it in the middle of the servers. So, to prevent this attack we use encryption and decryption, this will encrypt my data "hello" to Cipher Text and then it will send to my friend and again my friend decrypt it and make to readable form again.
Cipher Text is Look like for "hello" or for any other text or data is "yb6jf4fh88"
✱ Compression:- This will compress the large amount of data to less amount by deleting or removing un-neccesory bits from the file.
3. Session Layer
✱ Authentication:- Authentication is nothing but signup and login. When we open any application like Facebook, Instagram, or any other applications in which first we have to login with our username and password and then that application will open is called Authentication.
✱ Authorization:- After login with our username and password we get access of the application, we can read or write in that application that access is called Authorization.
✱ Check Pointing:- Have you ever downloaded anything from the web or from somewhere else? then you have noticed that your downloading file of 2GB and you paused it at 1.5GB or any other like at 1GB or 50MB and again you resume the download on the next day and its started downloading from where you have paused is called Check Pointing. It will restart from there where you have paused.
✱ Synchronization:- I think you have observed many time in the videos that lip-movement and audio is not matching, in some cases audio will come first and then lip-movement will happen and in sometimes lip-movement will happen first and then audio we listen is called Synchronization.
4. Transport Layer
✱ End to End It is also called as Port to Port. In the previous layer that is network layer will only transfer the data from one network host to another network host, but transport layer will take the total responsibility to transfer the data to the exact place, like we use many apps and websites at a time in the same device like whatsapp, instagram, facebook google, but transport layer will transfer the data at the exact location where sender want to send whethere it is whatsapp or facebbok or instagram or any other website etc..
✱ Conjunction Control or Flow Control
It will control the speed of the sending and receiving of data and also measures the time of transmission of data.. Because in some cases receiver has less speed of data transmission and sender has more speed of data transmission, in that case receiver can't bear it and data will be corrupted. So, on this case Flow Control will control the data transmission at the same speed to the both side.
It will control the speed of the sending and receiving of data and also measures the time of transmission of data.. Because in some cases receiver has less speed of data transmission and sender has more speed of data transmission, in that case receiver can't bear it and data will be corrupted. So, on this case Flow Control will control the data transmission at the same speed to the both side.
✱ Error Control:- This will use checksum to detect the errors after detecting we will see and try to control them. It uses checksum because on the software level we always use checksum and on the hardware level we use CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check).
✱ Multiplexing & De-multiplexing:- The is also a very important part of transport layer. Lets understand by an example:- Imagine you have a shop and you are bringing goods from the various companies and keeping in one place in your shop is called Multiplexing and again selling them to the different customers by there need is called De-Multiplexing.
5. Network Layer:- This layer will receive the data from the Transport Layer to and send to Data Link Layer.
✱ Host to Host
The first important thing in network layer is Host to Host or Source to Destination, This is used to transfer the data from one network topology host to another network topology host by using Logical Addressing (IP), Routing, Fragmentation and conjunction Control or Flow Control.
✱ Host to Host
The first important thing in network layer is Host to Host or Source to Destination, This is used to transfer the data from one network topology host to another network topology host by using Logical Addressing (IP), Routing, Fragmentation and conjunction Control or Flow Control.
Example:- If we are using Bus Topology and Star Topology, and now we want to send data from bus topology Device-D to star topology Device-H, then Device-D will send the data to Router with IP Address of Device-H and then router will pass it to the another router or directly to the Device-H if possible will the shortest path.
✱ Fragmentation:- If we are sending data from Device-A with the size of 100 mb to Device-B but Device-B capacity is only 20 mb per frame, then by using method fragmentation we divide 100 mb frame to 20 mb frame each and transmit to the Device-B
It will control the speed of the sending and receiving of data and also measures the time of transmission of data.. Because in some cases receiver has less speed of data transmission and sender has more speed of data transmission, in that case receiver can't bear it and data will be corrupted. So, on this case Flow Control will control the data transmission at the same speed to the both side.
6. Data Link Layer:- This layer will receive the data from the Network Layer in packets form. This layer also perform framing.
✱ What is framing
Data Link layer will organize or keep bits data into a Manageable Data Unit is called frames. Some times receiver won't get the actual amount which is send, it will be missing so in that case frame is very important to send the same amount of the data from the sender to receiver without missing anything.
✱ Physical Addressing (IP)
This will adds the header which contains the physical address of the sender and receiver. Physical address means Mac Address.
✱ Error Control
While transmission if any frame was corrupted or lost then the Data Link Layer will re-transmit that Particular frame again and again
✱ How Error Control finds the corruption or lost of frames?
It will run Frame Check Sequence (FCS) and check that the data was received perfectly without lost or corruption to the receiver or not, If not then it perform re-transmit to the particular frame by Header, Payload Field, Trailer.
✱ Conjunction Control or Flow Control
It will control the speed of the sending and receiving of data and also measures the time of transmission of data.. Because in some cases receiver has less speed of data transmission and sender has more speed of data transmission, in that case receiver can't bear it and data will be corrupted. So, on this case Flow Control will control the data transmission at the same speed to the both side.
7. Physical Layer:- This is the last layer of the OSI Model. This layer deals with the hardware like with Procedural, Electrical, Mechanical of physical link, for example cables and wires. This layer will receive the data from the Data Link layer as a Bits and convert it into the wired or cable signals and again from cable signals to bits signal to the receiver.
If you are using Optical Fiber for the physical link, then physical layer will convert it to the Light signal to transmit it.
If you are using Copper cable for the physical link, then physical layer will convert it to the Electrical signals to transmit it.
If you are using wireless for thr physical link, then physical layer will convert it to the Electro-Magnetic waves to transmit it.
Types of transmissions in the Physical Layer:-
1. Simplex:- This type of transmission will only send the signal to the receiver. This is the one-way root. It will only send, it can't receive again from the receiver.
Example:- TV and Antenna.
2. Half Duplex:- This type of transmission can send the signal to the receiver and also receive the signal from the receiver. But only if one point will stop sending then second point can send. They can't communicate at a same time.
Example:- walkie talkie.
3. Full Duplex:- This type of transmission can send and receive at the same time.
Example:- Mobile Phones.
Protocols are three levels:-
1. Hardware level
2. software level
3. Application level
Protocols are two type:-
1. Standard Protocol:- This is publicly available, anybody can use it. This will connect to the different devices and networks and transfers data.
Example:- FTP, DNS, DHCP, SMTP, TELENET, TFTP.
FTP:- File Transfer Protocol
DNS:- Domain Name System
DHCP:- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
SMTP:- Simple Mail Transfer
TELNET:- TELecomunication NETwork
TFTP:- Trivial File Transfer Protocol
2. Proprietary Protocol:- This is private. Only people who created this is only usable, if others want to use this they need to take permission of the owner if this. This will only send and recieve data from the same.
Example:- I Message to I Message, Apple Talk to Apple Talk.
✱ What is framing
Data Link layer will organize or keep bits data into a Manageable Data Unit is called frames. Some times receiver won't get the actual amount which is send, it will be missing so in that case frame is very important to send the same amount of the data from the sender to receiver without missing anything.
✱ Physical Addressing (IP)
This will adds the header which contains the physical address of the sender and receiver. Physical address means Mac Address.
✱ Error Control
While transmission if any frame was corrupted or lost then the Data Link Layer will re-transmit that Particular frame again and again
✱ How Error Control finds the corruption or lost of frames?
It will run Frame Check Sequence (FCS) and check that the data was received perfectly without lost or corruption to the receiver or not, If not then it perform re-transmit to the particular frame by Header, Payload Field, Trailer.
✱ Conjunction Control or Flow Control
It will control the speed of the sending and receiving of data and also measures the time of transmission of data.. Because in some cases receiver has less speed of data transmission and sender has more speed of data transmission, in that case receiver can't bear it and data will be corrupted. So, on this case Flow Control will control the data transmission at the same speed to the both side.
7. Physical Layer:- This is the last layer of the OSI Model. This layer deals with the hardware like with Procedural, Electrical, Mechanical of physical link, for example cables and wires. This layer will receive the data from the Data Link layer as a Bits and convert it into the wired or cable signals and again from cable signals to bits signal to the receiver.
If you are using Optical Fiber for the physical link, then physical layer will convert it to the Light signal to transmit it.
If you are using Copper cable for the physical link, then physical layer will convert it to the Electrical signals to transmit it.
If you are using wireless for thr physical link, then physical layer will convert it to the Electro-Magnetic waves to transmit it.
Types of transmissions in the Physical Layer:-
1. Simplex:- This type of transmission will only send the signal to the receiver. This is the one-way root. It will only send, it can't receive again from the receiver.
Example:- TV and Antenna.
2. Half Duplex:- This type of transmission can send the signal to the receiver and also receive the signal from the receiver. But only if one point will stop sending then second point can send. They can't communicate at a same time.
Example:- walkie talkie.
3. Full Duplex:- This type of transmission can send and receive at the same time.
Example:- Mobile Phones.
Protocols are three levels:-
1. Hardware level
2. software level
3. Application level
Protocols are two type:-
1. Standard Protocol:- This is publicly available, anybody can use it. This will connect to the different devices and networks and transfers data.
Example:- FTP, DNS, DHCP, SMTP, TELENET, TFTP.
FTP:- File Transfer Protocol
DNS:- Domain Name System
DHCP:- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
SMTP:- Simple Mail Transfer
TELNET:- TELecomunication NETwork
TFTP:- Trivial File Transfer Protocol
2. Proprietary Protocol:- This is private. Only people who created this is only usable, if others want to use this they need to take permission of the owner if this. This will only send and recieve data from the same.
Example:- I Message to I Message, Apple Talk to Apple Talk.
What is TCP/IP?
Full form of TCP/IP is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. This is the four layer architecture. It was developed by department of Defence Project Research Agency. This is used in current internet architecture instead of using OSI Reference Model.
Layers:-
2. Transport Layer:- This layer is same as in the OSI Reference Model, no changes implemented.
Full form of TCP/IP is Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. This is the four layer architecture. It was developed by department of Defence Project Research Agency. This is used in current internet architecture instead of using OSI Reference Model.
Layers:-
1. Application Layer:- This layer will cover the Presentation Layer and also Session Layer. In this TCP/IP Reference Model the presentation layer and session layer will get combined in application layer.
3. Inter-Network Layer:- This will work same as Network Layer like OSI Reference Model only lame has changed. Inter means Internet.
4. Data Link & Physical Layer:- This is also work same like in OSI Reference Model only thing is, it is combined both Data Link & Physical Layer.
Internet Protocol
There are two types of internet protocols
1. IPv4
✱ This is 32bit.
✱ This will only connect 4,294,967,295 Devices which is (2^32)
✱ This is consist of four numbers represented by dots
✱ Each number can range from 0 to 255 in decimal numbers, Also it is converted to binary code internally to make computer understandable.
✱ Each number is represented by group of eight binary digits
✱ Total IPv4 is represented by 32 ones and zero's
2. IPv6
✱ This is128 bit.
✱ This can connect 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 which is (2^128)
✱ Total IPv6 is represented by 128 ones and zero's
✱ This is human friendly
Classification of IP Address?
1. Dynamic IP Address:- This type of IP Address is not permanent it will always get change automatically when we disconnect and connect it again. It has very strong security.
2. Static IP Address:- This type of IP Address is permanent i will never change. It has less security.









No comments:
Post a Comment